A Retraction of the Original Research Article
Hydrogen-rich saline protects myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats
by Sun Q, Kang Z, Cai J, Liu W, Liu Y, Zhang JH, Denoble PJ, Tao H and Sun X (2009). Experimental Biology and Medicine. 234(10):1212–9. doi: 10.3181/0812-RM-349
Following publication, concerns were raised on the PubPeer platform regarding the integrity of the images in the published figures. Specifically, highlighted sections of the Sham and H2 images in Figure 6 appear to be duplicated.
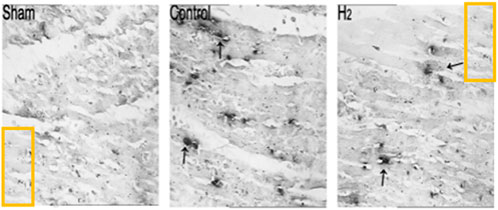
Figure 6. Detection of apoptotic cell death by TUNEL staining in the Sham, Control, and H2 groups at the end of 24 h of reperfusion. Relative to the Control group, H2 significantly reduced the number of TUNEL-positive cells (blue staining). Values are mean ± SEM; P < 0.01 compared to Control group, n = 6 for each group.
The authors remained unresponsive and failed to provide a satisfactory explanation during the investigation, which was conducted in accordance with Experimental Biology and Medicine’s policies. As a result, the data and conclusions of the article have been deemed unreliable, and the article has been retracted.
This retraction was approved by the Editor-in-Chief of Experimental Biology and Medicine. The authors received communication regarding the retraction. EBM would like to thank the users on PubPeer for bringing the published article to our attention.
Citation: EBM Editorial Office (2025) Retraction: Hydrogen-rich saline protects myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Exp. Biol. Med. 250:10605. doi: 10.3389/ebm.2025.10605
Received: 28 March 2025; Accepted: 02 April 2025;
Published: 10 April 2025.
Copyright © 2025 EBM Editorial Office. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: EBM Editorial Office, ZWJtQGVibS1qb3VybmFsLm9yZw==
 EBM Editorial Office
EBM Editorial Office